

Name
CALCIOBASE*
Active Substance
Calcium-citrate
The only calcium-citrate in a stick
-
- Gluten free
- Lactose free
- Sugar free
30 10 ml sticks of 500 mg calcium citrate each €15.80
*patented composition
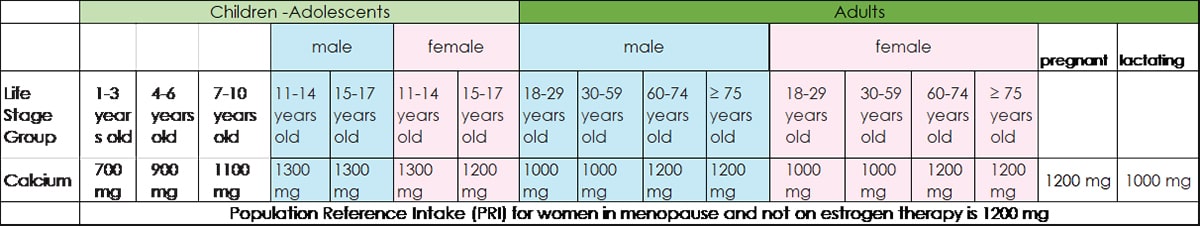 Source: Italian Society of Human Nutrition – SINU, 2014
Source: Italian Society of Human Nutrition – SINU, 2014 
WARNINGS: Food supplements are not intended as a substitute for a varied and balanced diet and a healthy lifestyle. Keep out of reach of children under 3 years. Do not exceed the recommended daily dose. Store in a cool and dry place at room temperature. Avoid exposure to light and direct sources of heat.
- Wilczynski C et al. Curr Osteoporos Rep 2014; 12: 396–402
- Iolascon G. et al J Nutr Health Aging 2017; 21: 527-538
- Heaney RP, et al J.Bone Miner Res1990; 5: 1135-1138
- Heaney et al J.Bone Miner Res. 2000; 15: 2291
- Hunt JN et al. Dig Dis Sci 1983; 28: 417-421
- Straub DA Nutr Clin Prac 2007; 22: 286-296






